Clarithromycin is used to treat certain bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and infections of the ears, sinuses, skin, and throat. It also is used to treat and prevent disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infection.
Clarithromycin is in a class of medications called macrolide antibiotics. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria. Antibiotics will not kill viruses that can cause colds, flu, or other infections.
How should this medicine be used?
Clarithromycin comes as a tablet, an extended-release (long-acting) tablet, and a suspension (liquid) to take by mouth. The regular tablet and liquid are usually taken with or without food every 12 hours (twice a day) for 7 to 14 days. The long-acting tablet is usually taken with food every 24 hours (once a day) for 7 to 14 days. Your doctor may tell you to take clarithromycin for a longer time depending on your condition. Take clarithromycin at around the same time(s) every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take clarithromycin exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
- Shake the suspension well before each use to mix the medication evenly.
- The tablets should be taken with a full glass of water. Swallow the long-acting tablets whole; do not split, chew, or crush them.
- You should begin to feel better during the first few days of treatment with clarithromycin. If your symptoms do not improve or get worse, call your doctor.
- Take clarithromycin until you finish the prescription, even if you feel better. If you stop taking clarithromycin too soon, or skip doses, your infection may not be completely treated and the bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.
Other uses for this medicine
Clarithromycin also is used sometimes to treat other types of infections including Lyme disease (an infection that may develop after a person is bitten by a tick), cryptosporidiosis (an infection that causes diarrhea), cat scratch disease (an infection that may develop after a person is bitten or scratched by a cat), Legionnaires' disease, (type of lung infection), and pertussis (whooping cough; a serious infection that can cause severe coughing). It is also sometimes used to prevent heart infection in patients having dental or other procedures. Talk to your doctor about the possible risks of using this medication for your condition.
This medication may be prescribed for other uses; ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
What special precautions should I follow?
Before taking clarithromycin,
- tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to clarithromycin, azithromycin (Zithromax), erythromycin ( Erythrocin), or any of the ingredients in clarithromycin tablets or suspension. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the ingredients.
- tell your doctor if you are taking astemizole,cisapride (Propulsid), colchicine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, lovastatin, simvastatin (Zocor, or terfenadine. Your doctor will probably tell you not to take clarithromycin if you are taking one or more of these medications.
- tell your doctor if you have or have ever had prolonged QT interval (a rare heart problem that may cause fainting or irregular heartbeat) or ventricular arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythms) or if you have ever had jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes) or other liver problems while taking clarithromycin, Your doctor will probably tell you not to take clarithromycin.
- tell your doctor and pharmacist what other prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking or plan to take. Be sure to mention any of the following: anticoagulants ('blood thinners') such as warfarin; certain benzodiazepines such as alprazolam (Xanax), midazolam, and triazolam (Halcion); bromocriptine (Parlodel); calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine, diltiazem, and verapamil (Isoptin); carbamazepine (Tegretol); certain medications for HIV such as atazanavir, didanosine, efavirenz, nevirapine, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, and zidovudine; certain medications for irregular heartbeat such as amiodarone (Cordarone), disopyramide, dofetilide, procainamide, quinidine, and sotalol; cholesterol-lowering medications (statins) such as atorvastatin (Lipitor), and rosuvastatin; cilostazol; cyclosporine (Neoral); darifenacin; digoxin; erlotinib (Tarceva); eszopiclone; fluconazole (Diflucan); insulin; itraconazole (Sporanox); methylprednisolone; omeprazole; oral medications for diabetes; phenytoin; ranitidine (Zantac); rifabutin; rifampin (Rifadin); rifapentine; sildenafil (Viagra); tacrolimus (Prograf); theophylline; tadalafil (Cialis); tolterodine; valproate; valproic acid; vardenafil (Levitra); and vinblastine. Many other medications may also interact with clarithromycin, so tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking, even those that do not appear on this list. Your doctor may need to change the doses of your medications or monitor you carefully for side effects.
- tell your doctor if you have a low level of magnesium or potassium in your blood, or if you have or have ever had an irregular heartbeat, or kidney, or liver disease.
- tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking clarithromycin, call your doctor.
- if you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist that you are taking clarithromycin.
What special dietary instructions should I follow?
Unless your doctor tells you otherwise, continue your normal diet.
What should I do if I forget a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember it. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue your regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed one.
What side effects can this medication cause?
Clarithromycin may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away:
Some side effects can be serious. If you experience any of the following symptoms, call your doctor immediately:
- rash
- hives
- itching
- swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, eyes, hands, feet, ankles, or lower legs
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- hoarseness
- peeling or blistering skin
- fever
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
- extreme tiredness
- unusual bleeding or bruising
- lack of energy
- loss of appetite
- pain in the upper right part of the stomach
- dark-colored urine
- flu-like symptoms
- fast, pounding, or irregular heartbeat
- muscle weakness such as difficulty chewing, talking, or performing daily activities
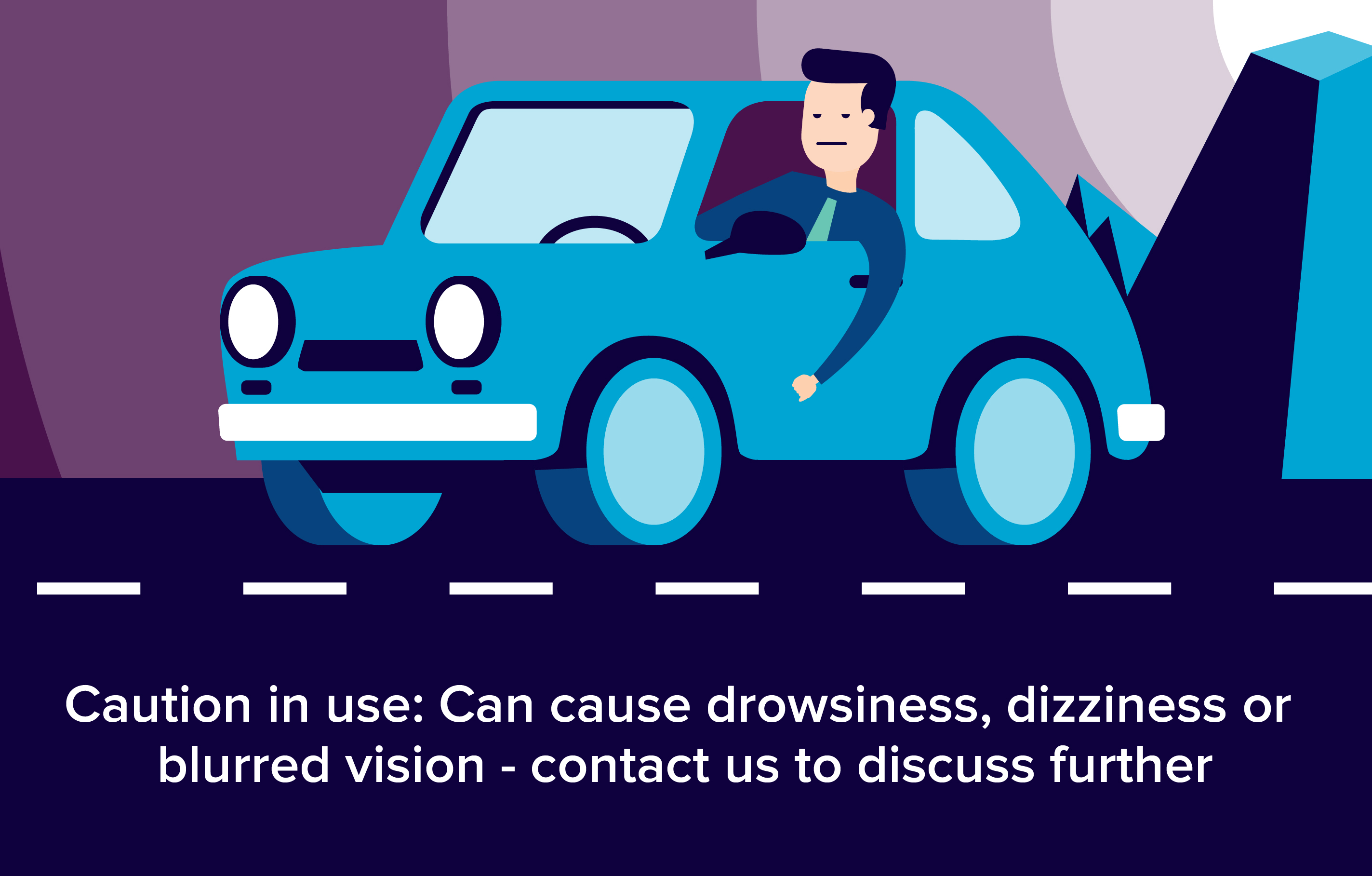
- double vision
Clarithromycin may cause other side effects. Call your doctor if you have any unusual problems while taking this medication.
What should I know about storage and disposal of this medication?
Keep this medication in the container it came in, tightly closed, and out of reach of children. Store the tablets at room temperature and away from light, excess heat, and moisture (not in the bathroom). Return medication that is outdated or no longer needed, to your local pharmacy. Do not refrigerate the suspension. Keep it at room temperature and away from excess heat and moisture. Throw away any unused suspension after 14 days. Talk to your pharmacist about the proper disposal of your medication.
In case of emergency/overdose
Symptoms of overdose may include the following:
- stomach pain
- nausea
- vomiting
- diarrhoea
What other information should I know?
The extended-release tablet does not dissolve in the stomach after swallowing. It slowly releases the medication as it passes through your digestive system. You may notice the tablet coating in the stool. This is normal and does not mean that you did not get the full dose of medication.
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Your prescription is probably not refillable. If you still have symptoms of infection after you finish the clarithromycin, call your doctor.
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription (over-the-counter) medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements.
If you have any more questions please ask your Pharmacist.
Remember to keep all medicines out of reach of children
Please Note: We have made every effort to ensure that the content of this information sheet is correct at time of publish, but remember that information about drugs may change. This sheet does not list all the uses and side-effects associated with this drug. For full details please see the drug information leaflet which comes with your medicine. Your doctor will assess your medical circumstances and draw your attention to any information or side-effects which may be relevant in your particular case.
References:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a692005.html
http://www.nhs.uk/medicine-guides/pages/selectorshow.aspx?medicine=clarithromycin
http://www.rxlist.com/biaxin-drug.htm
http://www.patient.co.uk/medicine/clarithromycin.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clarithromycin